Lab 4 Specifications
Introduction
In this lab you will learn how to write ARM assembly code to write a simple sorting algorithm.
Learning Objectives
By the end of this lab you will have:
- Written a simple assembly program to sort an array of signed bytes
- Used the debugger in SEGGER Embedded Studio to monitor a location in memory.
Requirements
Write an ARM assembly-language program to sort an array of 12 signed bytes on your MCU.
Resources
Specs
Open specifications in new tab.
Lab-specific Specifications
Proficiency
Excellence
General Specifications
Proficiency
General Schematic Specifications
Block Diagram
HDL & Code Specifications
General Formatting
Comments
Lab Writeup/Summary
Excellence
General Schematic Specifications
HDL & Code Specifications
General Formatting
Testbenches
Lab Writeup/Summary
Instructions
Project Setup
Set up a project in SEGGER Embedded Studio for your MCU. Once your project is created, download the starter code and put it in your src folder or create a new file inside your src directory titled sort.s and copy in the contents of the starter code.
Finish writing the assembly language subroutine under label main in sort.S to sort 12 signed bytes (the ones on the .byte … line under arr). Remember that assembly language code is nearly unreadable without line- by-line comments. If needed, use online reference sheets for ARM Thumb2 Assembly language (like the one linked on the course website) or refer to Chapter 6 of Digital Design and Computer Architecture.
Note: If you are running code on your Nucleo while it is connected to the development board, make sure that you remove the UPduino_+5V jumper to avoid powering the FPGA. Also note that you must have the MCU_+5V jumper connected in order to power the voltage regulators and ensure that the MCU reset signal is pulled high.
Running and Testing Your Code
Build your code and enter a debug session. With the MCU board connected via USB, start a debugging session by going to the debug section of the sidebar and pressing the green arrow in the top of the menu (or by using the keyboard shortcut F5).
Examine the memory location where the array of signed bytes has been loaded using the memory location viewer. The memory viewer is normally located near the bottom of the program window, but if you can’t find it, you can access it through the “View” menu in the program toolbar.
You may also choose to use the “Watch” section of the debugger. For example, if you want to view the contents of the byte array stored in memory, you can enter *(char[12] *) arr as a Watch expression. This tells the watch window to cast the address of the arr label to a pointer to a character and dereference 12 consecutive values from that memory location.
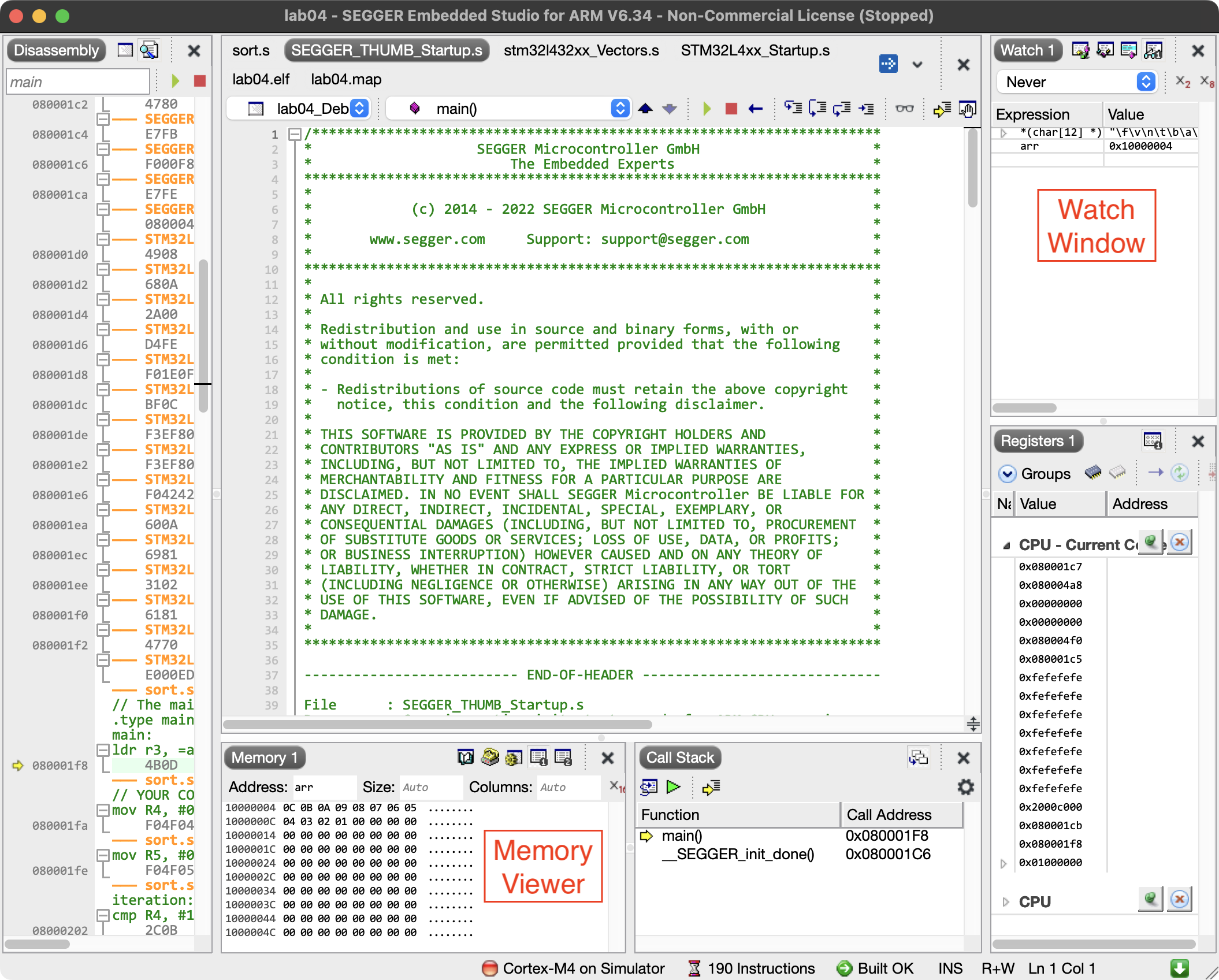
Step through the operation of your program and see how it changes the values of the array stored in memory.
To test your code, try various cases with the array in the .byte... line under the arr label. Rebuild and start a new debug session every time you make changes.
What to Turn In
- A short writeup of your design approach and the sort algorithm you chose to implement.
- A copy of your assembly code file sort.s.
- A listing of the test cases you used and the output of the tests. Be sure your tests would convince a skeptic that your algorithm works.
- For your lab checkoff, please have your lab set up and connected to a running debugger session so that the instructor may provide a test case for your code.
- How many hours did you spend on this lab?