Next: Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistors Up: ch4 Previous: Typical Transistor Circuits
Oscillation in a circuit is undesirable if the circuit is an amplifier or part of a control system which needs to be stable without oscillation. However, oscillation is desirable in many applications such as sinusoidal signal generator, carrier signal generation is broadcast transmission (radio and TV), clock signal in digital systems, etc.
An oscillator
is a feedback system composed of a forward path with gain


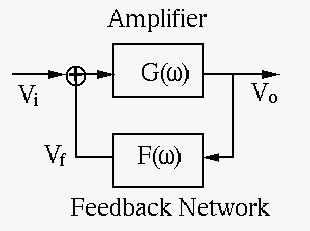
For the system to oscillate at a certain frequency, the feedback
needs to be positive for the frequency to be positively reinforced
while passing through the forward path in order to sustain the output




 |
(142) |
 is the open-loop gain and
is the open-loop gain and  is the closed-loop gain.
For this system to oscillate, i.e., for it to produce an output with
zero input, its closed-loop gain needs to be infinite, i.e., its
open-loop gain
is the closed-loop gain.
For this system to oscillate, i.e., for it to produce an output with
zero input, its closed-loop gain needs to be infinite, i.e., its
open-loop gain  need to be real, with zero phase
need to be real, with zero phase
 and unit gain
and unit gain  .
.
There exist many different configurations of oscillators based on a
single transistor. Shown below are three typical
Colpitts oscillators:
common-base (CB, left), common emitter (CE, middle), and common
collector (CC, right). All such circuits contain a “tank” LC circuit
composed of an inductor 


 where where |
(143) |
 is the equivalent capacitance of the series combination
of
is the equivalent capacitance of the series combination
of  and
and  . All other
. All other  s (without a subscript) are coupling
capacitors that have a large enough capacitance and can therefore be
treated as short circuit for AC signals.
s (without a subscript) are coupling
capacitors that have a large enough capacitance and can therefore be
treated as short circuit for AC signals.
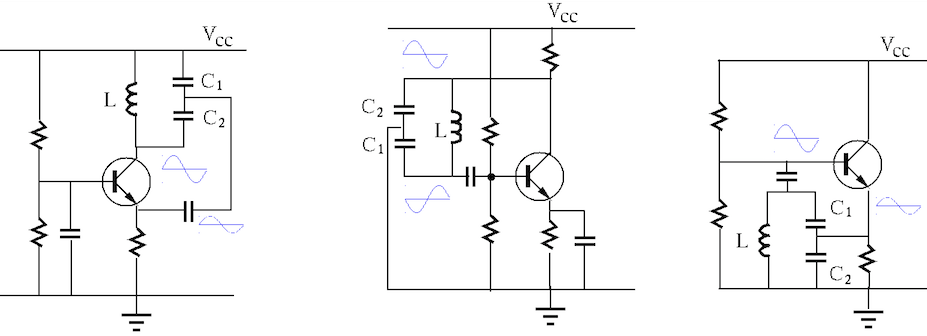
Here are the requirements for these circuits to oscillate:

 is the
output, a fraction of which at the middle point between the two
capacitors, “tap point”, is fed-back to the emitter to a positive
feedback loop:
is the
output, a fraction of which at the middle point between the two
capacitors, “tap point”, is fed-back to the emitter to a positive
feedback loop:
 |
(144) |
 is
the output, which is fed-back through the LC tank circuit to the base.
As the tap point is grounded, the sinusoidal voltage across the LC
tank produces opposite voltage polarities at the far ends of
is
the output, which is fed-back through the LC tank circuit to the base.
As the tap point is grounded, the sinusoidal voltage across the LC
tank produces opposite voltage polarities at the far ends of  and
and  , i.e.,
, i.e.,
 and
and
 have opposite phases
and thereby form a positive feedback loop:
have opposite phases
and thereby form a positive feedback loop:
 |
(145) |
 is the output that follows the input
voltage
is the output that follows the input
voltage  . The feedback from the emitter through the LC tank circuit
to the base form a positive feedback loop:
. The feedback from the emitter through the LC tank circuit
to the base form a positive feedback loop:
 |
(146) |
 is the voltage at the tap point.
is the voltage at the tap point.
More specifically, we consider the common-collector circuit as an example.
To find out why the circuit oscillates and the resonant frequency, we
disconnect the base path of the circuit and consider the open-loop gain
of 


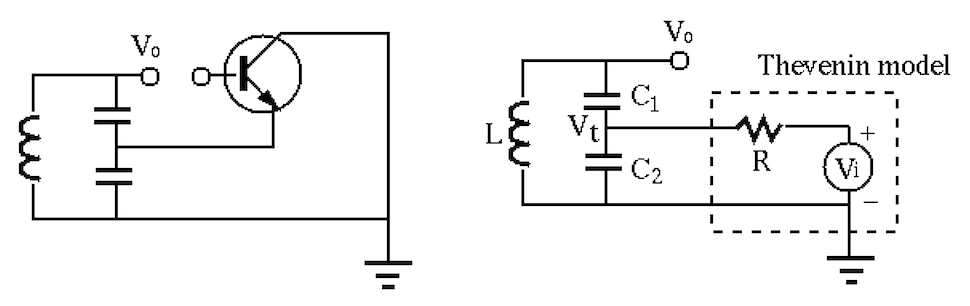
As the load of the Thevenin source, the tank circuit receives an input





 |
(147) |
 |
(148) |
 we get
we get
 |
(149) |
 i.e. i.e. |
(150) |
 is the resonant frequency, at which the voltage
is the resonant frequency, at which the voltage  become the same as the source voltage
become the same as the source voltage  , as the impedance of
the tank circuit as the load of the Thevenin source is infinity:
, as the impedance of
the tank circuit as the load of the Thevenin source is infinity:
 |
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
(151) |
 , the denominator becomes zeros and
, the denominator becomes zeros and
 ,
i.e., there is no current drawn from the source by the tank circuit.
Consequently, the voltage drop across
,
i.e., there is no current drawn from the source by the tank circuit.
Consequently, the voltage drop across  is zero and the voltage received
by the tank circuit is
is zero and the voltage received
by the tank circuit is  . Now the output voltage
. Now the output voltage  can be found
by voltage divider:
can be found
by voltage divider:
 i.e. i.e. |
(152) |
 to
to  ) is:
) is:
 |
(153) |
We see that when



