Next: Energy Dissipation/Storage in R, Up: Chapter 1: Basic Quantities Previous: Basic Quantities
In the following, we adopt the convention that a constant or
direct current (DC) or voltage is represented by an upper-case letter






Each of the three basic components resistor R, capacitor C, and inductor L can be described in terms of the relationship between the voltage across and the current through the component:
The voltage across and the current through a resistor are related by Ohm's law:
![$\displaystyle R=\frac{V}{I}=\frac{v}{i},\;\;\;\;\;\;\;[Ohm]=\frac{[Volt]}{[Ampere]},
\;\;\;\;\;\;\;
\Omega=\frac{V}{A}$](img90.svg) |
(19) |
 is the resistance of the conductor measured by Ohm
is the resistance of the conductor measured by Ohm
 (George Ohm (1789-1854)).
(George Ohm (1789-1854)).
The reciprocal of the resistance is the conductance:
![$\displaystyle G=\frac{1}{R}=\frac{I}{V}=\frac{i}{v},\;\;\;\;\;\;\;
[Siemens]=\frac{1}{[Ohm]}=\frac{[Ampere]}{[Volt]},
\;\;\;\;\;\;S=\frac{1}{\Omega}=\frac{A}{V}$](img93.svg) |
(20) |
![$[Siemens]=1/[Ohm]$](img94.svg) or
or
 (Werner von Siemens (1816-1892))
(Werner von Siemens (1816-1892))
A capacitor is composed of a pair of conductor plates separated by some
insulation material. The same amount of charge 
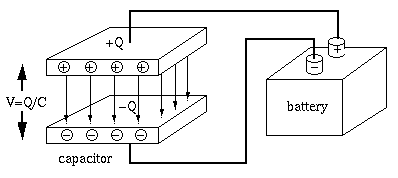
The voltage 


 |
(21) |
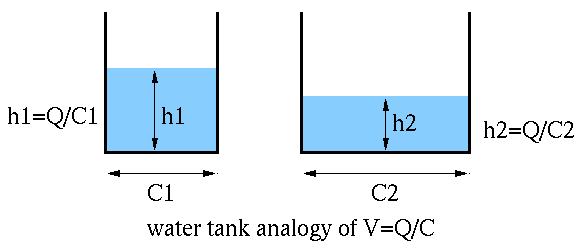
This relationship can be understood by considering the water tank
analogy of the capacitor. The capacity 









Why can an AC current “flow through” a capacitor composed of two insulated plates? Again consider the water tank analogy of the capacitor. If the pipeline is disconnected (an open circuit), no water flow (current) can go through. If two tanks are connected to the ends of the pipeline (a capacitor), and the pump drives the water in one direction (analogous to a DC voltage source), one of the tanks will fill up while the other one is empty (due to some initial current), there is still no continuous current. However, if the pump drives the water in alternative directions (analogous to AC voltage source), the water can flow through the pipeline, analogous to an AC current going through a capacitor (not through the insulation between its two plates).
The current through a capacitor can be found as:
 |
(22) |
 , and the capacitance
, and the capacitance
 represents the capacitor's capability to store charge
per unit voltage.
Capacitance
represents the capacitor's capability to store charge
per unit voltage.
Capacitance  is determined by the parameters of the capacitor:
is determined by the parameters of the capacitor:
 |
(23) |
 is the overlapping area of the plates and
is the overlapping area of the plates and  is the distance
between them, while
is the distance
between them, while  is the
permittivity (dielectric constant)
(the amount of charge needed
to generate one unit of electric flux) of the medium between the plates,
is the
permittivity (dielectric constant)
(the amount of charge needed
to generate one unit of electric flux) of the medium between the plates,
 is the
vacuum permittivity, and
is the
vacuum permittivity, and
 is the relative permitivity.
In an electrolytic capacitor, the gap between
the two plates is filled with dielectric medium of higher permittivity
so that the capacitance
is the relative permitivity.
In an electrolytic capacitor, the gap between
the two plates is filled with dielectric medium of higher permittivity
so that the capacitance  is increased.
is increased.

![$\displaystyle [Farad]=\frac{[Ampere][second]}{[Volt]} =\frac{[Coulomb]}{[Volt]},
\;\;\;\;\;\;\;
F=\frac{A\;s}{V}=\frac{C}{V}$](img111.svg) |
(24) |
 ,
,
 , and
, and
 .
.
Specially, when the voltage is sinusoidal

 |
(25) |
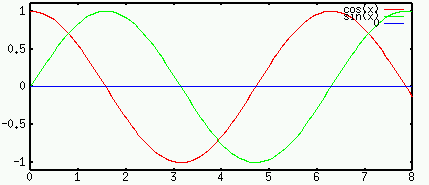
 of the voltage. In particular, for DC (
of the voltage. In particular, for DC ( ).
The current
).
The current
 is 0 (open circuit), and
when the frequency is very high (
is 0 (open circuit), and
when the frequency is very high (
 ), the
current
), the
current
 (short circuit).
(short circuit).
Magnetic field (flux) is generated in the space around a current flowing through a piece of conductor:
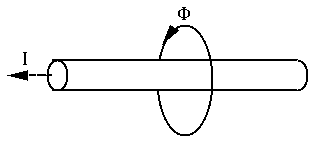
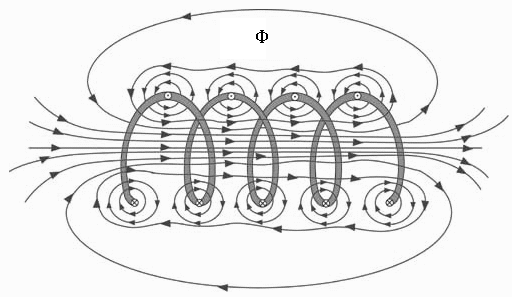
The magnetic field around a coil is the superposition of the magnetic flux generated by each section of the coil:
Electric current is induced in a conductor when there is changing magnetic flux in the surrounding space.
A time-varying electric current in a coil will cause a time-varying magnetic field in the surrounding space, which in turn will induce electric voltage and then current in the same coil (self-induction) or a different coil in the neighborhood (mutual-induction).
The self-induced voltage, the electromotive force (emf), across
the inductor coil due to a current 




 |
(26) |
 , and
, and
 is
the inductance of the inductor representing its capability to
produce magnetic flux per unit current.
Inductance
is
the inductance of the inductor representing its capability to
produce magnetic flux per unit current.
Inductance  is determined by the parameters of the inductor:
is determined by the parameters of the inductor:
 |
(27) |
 and
and  are respectively the cross section area and
length of the coil,
are respectively the cross section area and
length of the coil,  is the number of turns, and
is the number of turns, and  is the
magnetic permeability
(the ability of a material to support the
formation of a magnetic field within itself) of the medium inside
the coil. When a medium of high permeability, such as an iron core,
is inserted into the coil, its inductance
is the
magnetic permeability
(the ability of a material to support the
formation of a magnetic field within itself) of the medium inside
the coil. When a medium of high permeability, such as an iron core,
is inserted into the coil, its inductance  is increased.
is increased.
The unit of 
![$\displaystyle [Henry]=\frac{[Volt][second]}{[Ampere]},
\;\;\;\;\;\;\; H=\frac{Vs}{A}$](img131.svg) |
(28) |
 include
include
 and
and
 .
.
The polarity of the self-induced voltage 

When current 



Specially, when the current is sinusoidal

 |
(29) |
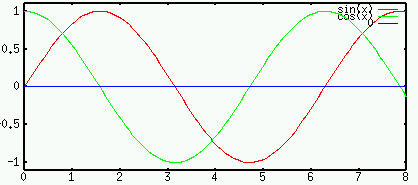
 of the current. In particular, for DC (
of the current. In particular, for DC ( ),
the voltage is 0 (short circuit), and when the frequency is very
high (
),
the voltage is 0 (short circuit), and when the frequency is very
high (
 ), the voltage
), the voltage
 (open circuit) for a finite
(open circuit) for a finite  .
.
From the above discussion, we see that for sinusoidal voltage and
current, the voltage across a capacitor is lagging behind the current
by 90 degrees, as it takes time to build up the charge




Note the following dimensionalities:
![$\displaystyle \left[\sqrt{\frac{L}{C}}\right]=\sqrt{\frac{[Henry]}{[Farad]}}
=\...
...nd]}{[Ampere]}\frac{[Volt]}{[second]\;[Ampere]}}
=\frac{[Volt]}{[Ampere]}=[Ohm]$](img141.svg) |
(30) |
![$\displaystyle \left[ \sqrt{LC} \right]=\sqrt{[Henry]\;[Farad]}
=\sqrt{\frac{[Volt]\;[second]}{[Ampere]}\frac{[Ampere]\;[second]}{[Volt]}}
=[second]$](img142.svg) |
(31) |
Comparing the relationships between the current through and voltage
across the three components below, we see that capacitance 



| Resistor |  |
 |
| Inductor |
 |
 |
| Capacitor |
 |
 |
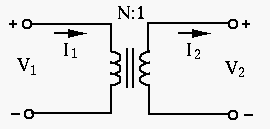
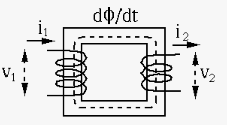
Two coils around a common iron core form a transformer. Assume the
primary coil has 




 goes through the
iron core of both primary and secondary coils;
goes through the
iron core of both primary and secondary coils;
 received by the primary
coil is is completely delivered to the secondary coil.
received by the primary
coil is is completely delivered to the secondary coil.
Faraday's Law: The voltage across a coil is proportional to the rate of change of the total magnetic flux:
 |
(32) |
 |
(33) |
 i.e., i.e., |
(34) |
 |
(35) |
 ,
then according Ohm's law, we have
,
then according Ohm's law, we have
 , and
, and
 |
(36) |