Next: Resistor, Capacitor, and Inductor Up: Chapter 1: Basic Quantities Previous: Chapter 1: Basic Quantities
 electrons is a
Coulomb, i.e., the charge each electron carries is
electrons is a
Coulomb, i.e., the charge each electron carries is
 Coulomb. Charge is
conservative (can be neither created nor destroyed).
Coulomb. Charge is
conservative (can be neither created nor destroyed).
 : Force can be defined by Newton's second law:
: Force can be defined by Newton's second law:
![$\displaystyle f=ma,\;\;\;\;\;\;\;[Newton]=\frac{[kilogram][meter]}{[second]^2}$](img4.svg) |
(1) |
 |
(2) |

![$[Newton\,(meter/kilogram)^2]$](img7.svg) is
the gravitational constant.
In particular, on surface of Earth, the “weight” of a mass
is
the gravitational constant.
In particular, on surface of Earth, the “weight” of a mass  is
is
 |
(3) |
 meter
meter second
second is the gravitational
acceleration that measures the intensity of Earth's gravitational field,
and
is the gravitational
acceleration that measures the intensity of Earth's gravitational field,
and  is the force this field asserts on mass
is the force this field asserts on mass  .
.
 |
(4) |

![$[Newton\,(meter/Coulumb)^2]$](img15.svg) is the
Coulomb's constant,
is the
Coulomb's constant,
 is the intensity of the electric
field caused by charge
is the intensity of the electric
field caused by charge  , and
, and  is the force this field asserts
on charge
is the force this field asserts
on charge  .
.
 , if a mass
, if a mass  (with weight
(with weight  ) is raised up from height
) is raised up from height
 to
to  , it receives a potential energy
, it receives a potential energy
![$\displaystyle w=fl=mg(h_2-h_1),\;\;\;\;\;\;g=\frac{w}{m(h_2-h_1)},\;\;\;\;
\frac{[Joule]}{[kilogram][meter]}=\frac{[Newton]}{[kilogram]}
=\frac{[meter]}{[s]^2}$](img23.svg) |
(5) |
 , if
a charge
, if
a charge  is moved along the direction of the field from point
is moved along the direction of the field from point  to point
to point  , it receives a potential energy
, it receives a potential energy
![$\displaystyle w=fl=qE(l_2-l_1),\;\;\;\;\;\;E=\frac{w}{q(l_2-l_1)},\;\;\;\;
\frac{[Joule]}{[Coulomb][meter]}=\frac{[Newton]}{[Coulomb]}$](img28.svg) |
(6) |
 Ampere Ampere![$\displaystyle ]=\frac{[Coulomb]}{[second]}$](img30.svg) |
(7) |
The current is the same through out an electricity conducting component, it is a through variable.
Current density

 |
(8) |
![$\displaystyle v=v-v_0=\frac{w}{q}=\frac{Eq(l-l_0)}{q}=E(l-l_0),
\;\;\;\;[Volt]=\frac{[Joule]}{[Coulomb]}$](img33.svg) |
(9) |
 (a reference point or “ground”) is
(a reference point or “ground”) is  by definition. The voltage is the difference between two potential energy
levels
by definition. The voltage is the difference between two potential energy
levels  and
and  per unit charge in an electric field. A unit charge
of
per unit charge in an electric field. A unit charge
of  Coulomb moved from one electric potential
Coulomb moved from one electric potential  to another
to another
 gains a potential energy
gains a potential energy
 |
(10) |
 |
(11) |
 Coulomb is moved through an electric field
Coulomb is moved through an electric field
 of 1 volt, it receives or delivers 1 Joule of energy.
of 1 volt, it receives or delivers 1 Joule of energy.
Voltage 

The voltage is measured as the difference across two points in an electric field or circuit (or a point with respect to a reference point called ground), i.e., it is an across variable.
Power 
![$\displaystyle p=\frac{dw}{dt}=\frac{dw}{dq} \; \frac{dq}{dt}=v\,i,
\;\;\;\;\;\;...
...{[second]}
=\frac{[Joule]}{[Coulomb]}\frac{[Coulomb]}{[second]}
=[Volt][Ampere]$](img47.svg) |
(12) |
![$\displaystyle w=\int p\;dt=\int vi\;dt,
\;\;\;\;[Joule]=[Watt][second]=[Volt][Ampere][second]$](img48.svg) |
(13) |
 hp
hp Watts
Watts
Energy can also be measured by kilowatt-hours (kWh)

The energy needed to move a charge 


 |
(14) |
 is the potential difference
between the two points.
is the potential difference
between the two points.
An electric field

The energy needed to move a mass 




 |
(15) |
 is the potential difference between the
two heights.
The Gravitational field
is the potential difference between the
two heights.
The Gravitational field
 is the gravitational potential
difference per unit distance.
is the gravitational potential
difference per unit distance.
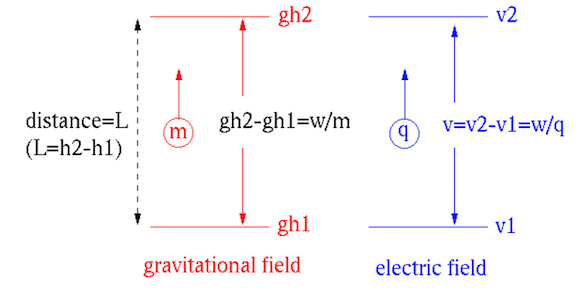
 ;
Energy per unit charge is voltage
;
Energy per unit charge is voltage
 is voltage.
is voltage.
 ;
Energy per unit mass is
;
Energy per unit mass is
 . Although this quantity is not
explicitly defined, it is analogous equivalent to voltage in electric
field.
. Although this quantity is not
explicitly defined, it is analogous equivalent to voltage in electric
field.
| Force |

 |

 |
| Field intensity |
 |
 |
| Potential difference |  |
 |
| Potential energy |
 |
 |
The intensity of magnetic effect (lines per unit area in a magnetic
field or flux) is measured by magnetic flux density 
The magnetic flux 

![$\displaystyle \Phi=\int {\bf B} \cdot d{\bf A}=\vert B\vert\;\vert A\vert \cos\alpha,\;\;\;\;
[Weber]=[Tesla] [meter]^2$](img77.svg) |
(16) |
 is the angle between the two directions.
is the angle between the two directions.
When 





In a magnetic field 



![$\displaystyle {\bf f}=q{\bf u} \times {\bf B},\;\;\;\;\;
[Newton]=[Coulomb]\frac{[meter]}{[second]} [Tesla]$](img82.svg) |
(17) |
 is the cross product of velocity vector
is the cross product of velocity vector
 and magnetic flux vector
and magnetic flux vector  (right-hand rule).
(right-hand rule).
A force of 1 Newton is experienced by a charge of 1 Coulomb moving with a velocity of 1 meter per second normal to a magnetic flux density of 1 Tesla.
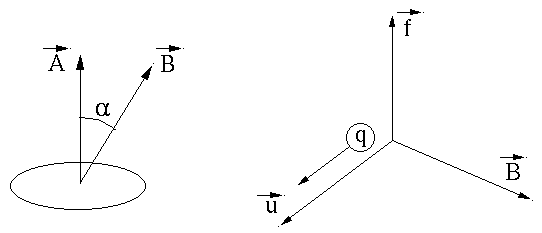
The Lorentz force
on a charge 
 |
(18) |