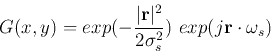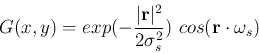
The Gabor model can also be viewed in the spatial frequency domain. Given the Gabor function
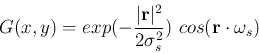
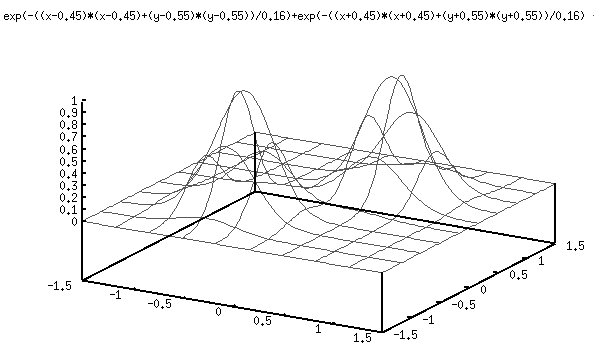
Similar to using the Gaussian model to predict the spatial response properties of the center-surround receptive field of the ganglion cells, here we can use the Gabor model of the simple V1 cells to predict their spatial response properties. From the spectrum of the Gabor function we see that a V1 simple cell also behaves like a band-pass filter that favors spatial frequencies within a certain range. However, different from the center-surround ganglion cells, the V1 cells are also selective to the orientations, as can be seen in the spatial domain discussed previously, and also in spatial frequency domain where the two peaks of the spectrum (central symmetric with respect to the origion) indicate the orientation preference of the V1 cell modeled as a filter.
For mathematical convenience, we include an imaginary part
![]() in the Gabor model so
that it can be written as (by Euler formula):
in the Gabor model so
that it can be written as (by Euler formula):