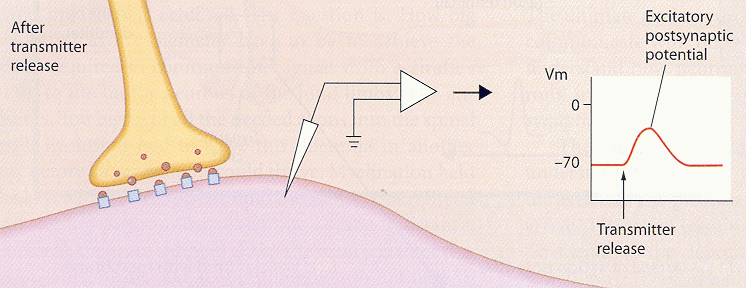
The chemical interaction of the neurotransmitter and the postsynaptic receptor initiates events that lead to either depolarization (excitation) or hyperpolarization (inhibition) of the postsynaptic cell. If this cell is a neuron, an excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP) can lead to the generation of action potentials in this neuron. If this cell is a muscle cell, the EPSP leads to action potentials in the muscle and muscle contraction. If the postsynaptic membrane potential is hyperpolarized, the postsynaptic cell is less likely to generate an action potential and is inhibited.
