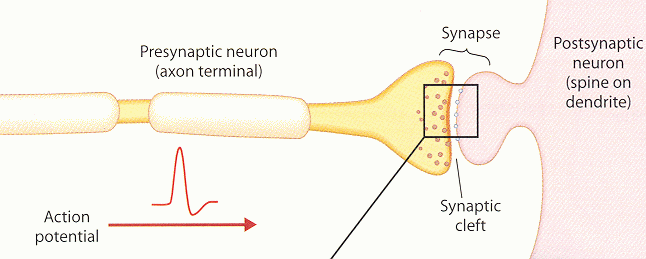
An action potential arriving at the axon terminal depolarizes the terminal
region and initiates an influx of Ca++ ions into the region. As a result,
small vesicles containing neurotransmitter fuse with the membrane at the
synapse and release this transmitter into the synaptic cleft, the space
between the presynaptic and postsynaptic neuronal membranes. Crossing the
cleft by diffusion, the transmitter arrives at the postsynaptic membrane
and binds and interact with the receptor molecules embedded in the membrane.
