


Next: Physical Meaning of 2-D
Up: fourier
Previous: Fourier Transform 2 Real
Two-dimensional Fourier transform also has four different forms depending on
whether the 2D signal (usually spatial signal) 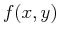 is periodic and
whether it is discrete.
is periodic and
whether it is discrete.
- Non-periodic, continuous signal
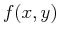 ,
continuous, non-periodic spectrum
,
continuous, non-periodic spectrum 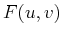
where 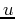 and
and 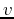 are spatial frequencies in
are spatial frequencies in 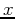 and
and 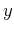 directions,
respectively, and
directions,
respectively, and 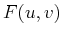 is the 2D spectrum of
is the 2D spectrum of 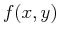 .
.
- Non-periodic, discrete signal
![$f[m,n]$](img207.png) ,
continuous, periodic spectrum
,
continuous, periodic spectrum 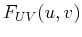
where 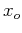 and
and 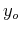 are the spatial intervals between consecutive signal
samples in the
are the spatial intervals between consecutive signal
samples in the 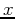 and
and 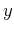 directions, respectively, and
directions, respectively, and 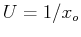 and
and
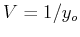 are sampling rates in the two directions, and they are also the
periods of the spectrum
are sampling rates in the two directions, and they are also the
periods of the spectrum 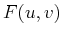 .
.
- Periodic, continuous signal
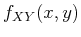 ,
discrete, non-periodic spectrum
,
discrete, non-periodic spectrum ![$F[k,l]$](img216.png)
where 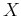 and
and 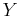 are periods of the signal in
are periods of the signal in 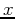 and
and 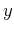 directions,
respectively, and
directions,
respectively, and 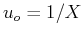 and
and 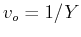 are the intervals between
consecutive samples in the spectrum
are the intervals between
consecutive samples in the spectrum ![$F[k,l]$](img216.png) .
.
- Periodic, discrete signal
![$f[m,n]$](img207.png) , discrete and periodic
spectrum
, discrete and periodic
spectrum ![$F[k,l]$](img216.png)
where 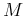 and
and 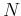 are the numbers of samples in
are the numbers of samples in 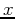 and
and 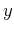 directions,
respectively, and
directions,
respectively, and ![$X[k,l]$](img227.png) is the 2D discrete spectrum of
is the 2D discrete spectrum of ![$x[m,n]$](img228.png) . Both
. Both
![$X[k,l]$](img227.png) and
and ![$x[m,n]$](img228.png) can be considered as elements in two
can be considered as elements in two 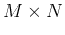 matrices
matrices
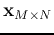 and
and
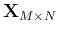 , respectively.
, respectively.



Next: Physical Meaning of 2-D
Up: fourier
Previous: Fourier Transform 2 Real
Ruye Wang
2015-11-12
![]() is periodic and
whether it is discrete.
is periodic and
whether it is discrete.
![\begin{displaymath}
F_{UV}(u,v)=\sum_{m=-\infty}^{\infty} \sum_{n=-\infty}^{\infty}
f[m,n]e^{-j2\pi(umx_o+vny_o)}
\end{displaymath}](img209.png)
![\begin{displaymath}f_{XY}(x,y)=\sum_{k=-\infty}^{\infty} \sum_{l=-\infty}^{\infty} F[k,l]
e^{-j2\pi(xku_o+ylv_o)} \end{displaymath}](img218.png)
![\begin{displaymath}X[k,l]=\frac{1}{\sqrt{MN}}\sum_{n=0}^{N-1}\sum_{m=0}^{M-1}x[m,n]
e^{-j2\pi(\frac{mk}{M}+\frac{nl}{N})} \end{displaymath}](img223.png)
![\begin{displaymath}x[m,n]=\frac{1}{\sqrt{MN}}\sum_{l=0}^{N-1}\sum_{k=0}^{M-1}X[k,l]
e^{j2\pi(\frac{mk}{M}+\frac{nl}{N})} \end{displaymath}](img224.png)