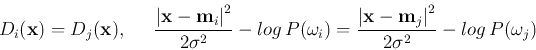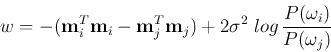Next: The AdaBoost Algorithm
Up: Bayes Classifier
Previous: Error analysis
If
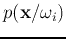 can be assumed to be a normal distribution, the
discriminant function can be written as:
can be assumed to be a normal distribution, the
discriminant function can be written as:
Since 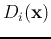 is used only relatively among all classes, it can be
replaced by a monotonic log function and the discriminant function becomes
is used only relatively among all classes, it can be
replaced by a monotonic log function and the discriminant function becomes
The second term
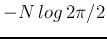 is a constant common to all classes and
can therefore be dropped and the discriminant function is
is a constant common to all classes and
can therefore be dropped and the discriminant function is
This is the most general case and the boundary between any two classes
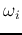 and
and 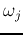 is described by
is described by
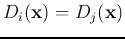 , i.e.,
, i.e.,
is a quadric (multi-variable quadratic) equation:
where 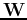 is an n by n matrix:
is an n by n matrix:
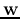 is an n by 1 vector:
is an n by 1 vector:
and 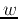 is a scalar:
is a scalar:
These boundaries in the N-D feature space are in general quadric hyper-surfaces,
such as hyper-sphere, hyper-ellipsoid, hyper-parabola, hyper-hyperbola, etc.
Now consider several special cases:



Next: The AdaBoost Algorithm
Up: Bayes Classifier
Previous: Error analysis
Ruye Wang
2016-11-30
![]() can be assumed to be a normal distribution, the
discriminant function can be written as:
can be assumed to be a normal distribution, the
discriminant function can be written as:
![\begin{displaymath}
D_i({\bf x})=P(\omega_i)p({\bf x}/\omega_i)
=P(\omega_i)\; \...
... x}-{\bf m}_i)^T {\bf\Sigma}_i^{-1}({\bf x}-{\bf m}_i)\right]
\end{displaymath}](img168.png)
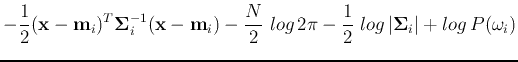
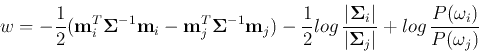
![]() between
between ![]() and
and ![]() becomes
becomes
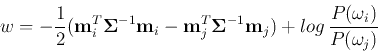
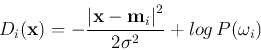
![]() and
and ![]() is:
is: