


Next: Singular value decomposition
Up: algebra
Previous: Generalized eigenvalue problem
Theorem: The product of two unitary matrices is unitary.
Proof: Let 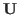 and
and 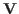 be unitary, i.e.,
be unitary, i.e.,
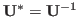 and
and
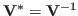 , then
, then
 is unitary:
is unitary:
Theorem: Two square matrices 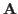 and
and 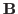 are simultaneously
diagonalizable if and only if they commute.
are simultaneously
diagonalizable if and only if they commute.
Proof
(reference)
Theorem: A matrix is normal if and only if it is unitarily diagonalizable.
Proof
(reference)
- If
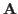 is unitarily diagonalizable:
is unitarily diagonalizable:
where
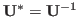 is unitary and
is unitary and 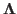 is a diagonal
matrix satisfying
is a diagonal
matrix satisfying
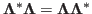 ,
then
,
then 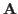 is normal:
is normal:
- If
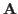 is normal, then it is diagonalizable by a unitary matrix.
First we show any matrix
is normal, then it is diagonalizable by a unitary matrix.
First we show any matrix 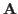 can be written as
can be written as
where
are both Hermitian, and diagonalizable by a unitary matrix.
As 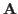 is normal, we have
is normal, we have
We see that
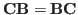 , i.e.,
, i.e., 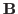 and
and 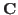 commute, and they can be simultaneously diagonalized by some unitary matrix
commute, and they can be simultaneously diagonalized by some unitary matrix
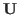 :
:
and so can
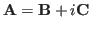 :
:



Next: Singular value decomposition
Up: algebra
Previous: Generalized eigenvalue problem
Ruye Wang
2015-04-27
![]() and
and ![]() be unitary, i.e.,
be unitary, i.e.,
![]() and
and
![]() , then
, then
![]() is unitary:
is unitary:
![]() and
and ![]() are simultaneously
diagonalizable if and only if they commute.
are simultaneously
diagonalizable if and only if they commute.