


Next: Normal matrices and diagonalizability
Up: algebra
Previous: Eigenvalues and matrix diagonalization
The generalized eigenvalue problem of two symmetric matrices
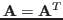 and
and
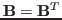 is to find a scalar
is to find a scalar 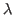 and the corresponding vector
and the corresponding vector 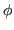 for the following equation to hold:
for the following equation to hold:
or in matrix form
The eigenvalue and eigenvector matrices 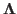 and
and 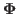 can be found in the following steps.
can be found in the following steps.
The Rayleigh quotient of two symmetric matrices 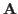 and
and 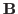 is a function of a vector
is a function of a vector 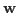 defined as:
defined as:
To find the optimal 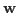 corresponding to the extremum (maximum or minimum)
of
corresponding to the extremum (maximum or minimum)
of  , we find its derivative with respect to
, we find its derivative with respect to 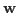 :
:
Setting it to zero we get
The second equation can be recognized as a generalized eigenvalue problem with
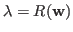 being the eigenvalue and and
being the eigenvalue and and 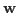 the corresponding
eigenvector. Solving this we get the vector
the corresponding
eigenvector. Solving this we get the vector
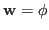 corresponding
to the maximum/minimum eigenvalue
corresponding
to the maximum/minimum eigenvalue
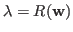 , which maximizes/minimizes
the Rayleigh quotient.
, which maximizes/minimizes
the Rayleigh quotient.



Next: Normal matrices and diagonalizability
Up: algebra
Previous: Eigenvalues and matrix diagonalization
Ruye Wang
2015-04-27
![]() and
and
![]() is to find a scalar
is to find a scalar ![]() and the corresponding vector
and the corresponding vector ![]() for the following equation to hold:
for the following equation to hold:
![]() is symmetric,, it can be diagonalized by its orthogonal
eigenvector matrix
is symmetric,, it can be diagonalized by its orthogonal
eigenvector matrix ![]() :
:
![]() and
and ![]() is a function of a vector
is a function of a vector ![]() defined as:
defined as: