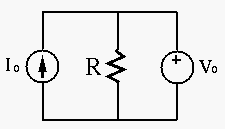
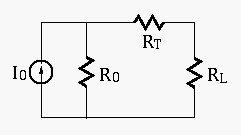
To verify your choice of load resistance, show that the power consumption of the load will always be lower than this maximum when its resistance is either increased or decreased by ten percent.
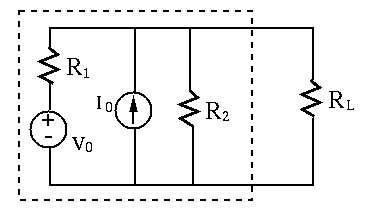
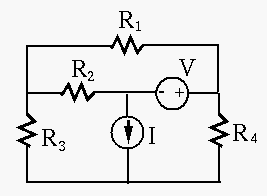


To verify your choice of load resistance, show that the power consumption of the load will always be lower than this maximum when its resistance is either increased or decreased by ten percent.

