- Inverting amplifier
Find the input resistance  , output resistance
, output resistance  and open-voltage gain
and open-voltage gain  of the inverting amplifier. (Read
and understand the derivation shown in the lecture notes.)
of the inverting amplifier. (Read
and understand the derivation shown in the lecture notes.)
- Non-inverting amplifier
Find the input resistance  , output resistance
, output resistance  and open-voltage gain
and open-voltage gain  of the non-inverting amplifier,
and compare your results with those given at the bottom of
this page.
of the non-inverting amplifier,
and compare your results with those given at the bottom of
this page.
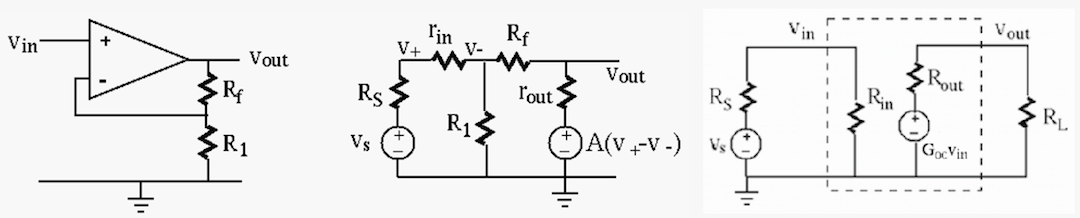
- Algebraic summer:
Express the output voltage  as a weighted sum of the four
input voltages
as a weighted sum of the four
input voltages
 :
:
Find the four coefficients (may be either positive or negative).
Hint: Define
 , and apply KCL to
, and apply KCL to  and
and  to get two equations. Solve one of them for
to get two equations. Solve one of them for  , substitute it into
the other equation, and then write
, substitute it into
the other equation, and then write  as a function of all
four input voltages.
as a function of all
four input voltages.
The algebraic summer can be generalized to have  inputs
inputs  all connected through
all connected through  (
(
 ) to the inverting input
of the op-amp, and
) to the inverting input
of the op-amp, and  inputs
inputs  all connected through
all connected through  (
(
 ) to the non-inverting input of the op-amp. Give
the general expression of the output
) to the non-inverting input of the op-amp. Give
the general expression of the output  as a function of all
as a function of all
 inputs in terms of all resistors
inputs in terms of all resistors  resistors.
resistors.
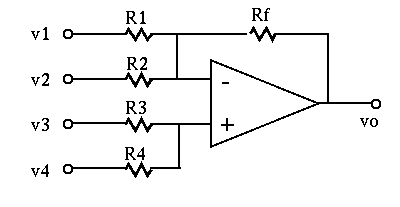
- Sallen-Key filter (HP/LP)
Derive the voltage gain (
 ) of the general Sallen-Key
fitler (HP or LP) in terms of the impedances
) of the general Sallen-Key
fitler (HP or LP) in terms of the impedances  through
through  :
:
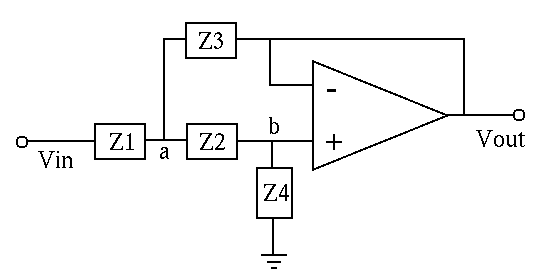
- Sallen-Key filter (BP)
Derive the voltage gain (
 ) of the general Sallen-Key
fitler (HP or LP) in terms of the impedances
) of the general Sallen-Key
fitler (HP or LP) in terms of the impedances  through
through  and
and  ,
,  ,
,  .
.
(Hint: For simplicity, assume
 .
.
- The Howland current source:
The circuit generates a constant current through the load, independent
of the load resistance  of the load. Give the expression of this
current
of the load. Give the expression of this
current  through
through  as a function of the inputs
as a function of the inputs  and
and  and the resistances in the circuit, and show it is independent of
and the resistances in the circuit, and show it is independent of  .
Assume
.
Assume
 .
.
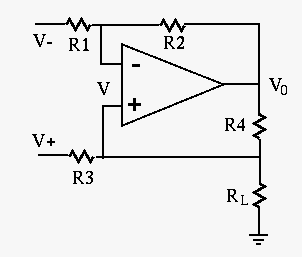
Hint: recall the relationship between the current through and voltage
across a diode and use the virtual ground assumption.
- Exponential and logarithmic amplifiers:
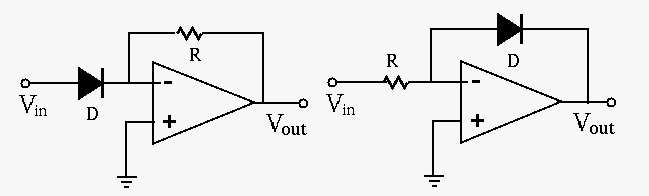
The current  through and voltage
through and voltage  across a diode are related
by the following:
across a diode are related
by the following:
where  and
and  are some parameters. The direction of the current
are some parameters. The direction of the current
 through the diode is indicated by the arrow of the symbol, and the
polarity of the voltage
through the diode is indicated by the arrow of the symbol, and the
polarity of the voltage  is plus on the arrow side and minus on the
other side. When
is plus on the arrow side and minus on the
other side. When
 is large enough,
is large enough,
 .
.
Show that the output voltages  of the exponential amplifier
(left) and logarithmic amplifier (right) are approximately an exponential
and logarithmic function of the input voltage
of the exponential amplifier
(left) and logarithmic amplifier (right) are approximately an exponential
and logarithmic function of the input voltage  , respectively:
, respectively:
Derive these relationships and determine the coefficients  and
and
 .
.



















































 and
and  are some parameters. The direction of the current
are some parameters. The direction of the current
 through the diode is indicated by the arrow of the symbol, and the
polarity of the voltage
through the diode is indicated by the arrow of the symbol, and the
polarity of the voltage  is plus on the arrow side and minus on the
other side. When
is plus on the arrow side and minus on the
other side. When
 is large enough,
is large enough,
 .
.



 and
and
 .
.