


Next: Appendix C: Matrix Operations
Up: MCMC
Previous: Appendix A: Kullback-Leibler (KL)
The case of two terms in the summation can be shown graphically. An
arbitrary point 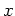 between
between 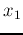 and
and 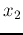 can be expressed as
can be expressed as
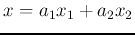 with the weighting coefficients
with the weighting coefficients 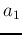 and
and 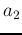 satisfying
satisfying 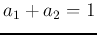 . The weighted average
. The weighted average
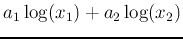 of
of 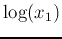 and
and 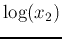 is on the straight line between
is on the straight line between
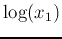 and
and 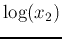 , below the point on the log function
, below the point on the log function
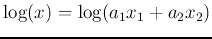 , i.e.,
, i.e.,
The equal sign only holds when either of the two weights is 1 and the
other is 0. This result can be generalized to multiple terms in the
weighted sum, the average of log functions of multiple 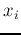 's is
always no greater than the log of the average of these
's is
always no greater than the log of the average of these 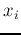 's.
's.
Ruye Wang
2018-03-26