A vector space is a set ![]() with two operations of addition and
scalar multiplication defined for its members, referred to as vectors.
with two operations of addition and
scalar multiplication defined for its members, referred to as vectors.
- Vector addition maps any two vectors
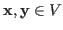 to another vector
to another vector
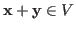 satisfying the following
properties:
satisfying the following
properties:
- Commutativity:
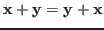 .
.
- Associativity:
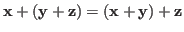 .
.
- Existence of zero: there is a vector
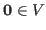 such that:
such that:
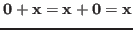 .
.
- Existence of inverse: for any vector
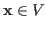 , there is
another vector
, there is
another vector 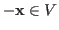 such that
such that
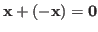 .
.
- Commutativity:
- Scalar multiplication maps a vector
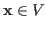 and a real
or complex scalar
and a real
or complex scalar 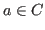 to another vector
to another vector
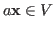 with the following properties:
with the following properties:
-
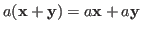 .
.
-
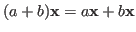 .
.
-
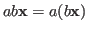 .
.
-
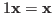 .
.
-
Listed below is a set of typical vector spaces for various types of signal of interest.
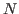 -D vector space
-D vector space 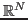 or
or 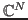
This space contains all
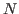 -D vectors expressed as an
-D vectors expressed as an 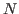 -tuple, an ordered
list of
-tuple, an ordered
list of 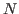 elements (or components):
elements (or components):
![\begin{displaymath}
{\bf x}=\left[ \begin{array}{c}x_1 x_2 \vdots x_N \end{array} \right]
=[x_1,x_2,\ldots,x_N]^T,
\end{displaymath}](img20.png)
which can be used to represent a discrete signal containing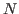 samples.
We will always represent a vector as a column vector, or the transpose of
a row vector. The space is denoted by either
samples.
We will always represent a vector as a column vector, or the transpose of
a row vector. The space is denoted by either 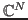 if the elements
are complex
if the elements
are complex
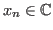 , or
, or 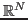 if they are all real
if they are all real
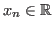 (
(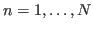 ).
).
- A vector space can be defined to contain all
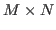 matrices composed
of
matrices composed
of 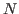
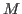 -D column vectors:
-D column vectors:
![\begin{displaymath}
{\bf A}=[{\bf a}_1,\ldots,{\bf a}_N]
=\left[ \begin{array}...
...\
x_{M,1} & x_{M,2} & \cdots & x_{M,N} \end{array} \right],
\end{displaymath}](img26.png)
where the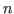 th column is an
th column is an 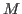 -D vector
-D vector
![${\bf a}_n=[x_{1,n},\ldots,x_{M,n}]^T$](img28.png) .
Such a matrix can be converted to an
.
Such a matrix can be converted to an 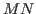 -D vector by cascading all of the
column (or row) vectors.
-D vector by cascading all of the
column (or row) vectors.
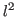 space:
space:
The dimension
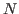 of
of 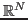 or
or 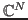 can be extended
to infinity so that a vector in the space becomes a sequence
can be extended
to infinity so that a vector in the space becomes a sequence
![${\bf x}=[\ldots,x_n,\ldots]^T$](img31.png) for
for
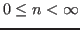 or
or
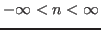 .
If all vectors are square-summable, the space is denoted by
.
If all vectors are square-summable, the space is denoted by 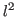 . All
discrete energy signals are vectors in
. All
discrete energy signals are vectors in 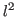 .
.
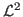 space:
space:
A vector space can also be a set of real or complex valued continuous functions
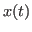 defined over either a finite range such as
defined over either a finite range such as 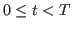 ,
or an infinite range
,
or an infinite range
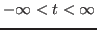 . If all functions are square-integrable,
the space is denoted by
. If all functions are square-integrable,
the space is denoted by 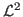 . All continuous energy signals are vectors
in
. All continuous energy signals are vectors
in 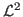 .
.
Note that the term ``vector'', generally denoted by ![]() , may be interpreted
in two different ways. First, in the most general sense, it represents a member
of a vector space, such as any of the vector spaces considered above; e.g., a
function
, may be interpreted
in two different ways. First, in the most general sense, it represents a member
of a vector space, such as any of the vector spaces considered above; e.g., a
function
![]() . Second, in a more narrow sense, it can
also represent a tuple of
. Second, in a more narrow sense, it can
also represent a tuple of ![]() elements, an
elements, an ![]() -D vector
-D vector
![]() , where
, where ![]() may be infinity. It
should be clear what a vector
may be infinity. It
should be clear what a vector ![]() represents from the context.
represents from the context.
An inner product in a vector space ![]() is a function that
maps two vectors
is a function that
maps two vectors
![]() to a scalar
to a scalar
![]() and
satisfies the following conditions:
and
satisfies the following conditions:
- Positive definiteness:
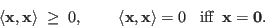
- Conjugate symmetry:
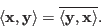
If the vector space is real, the inner product becomes symmetric:
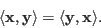
- Linearity in the first variable:
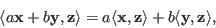
where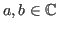 . The linearity does not apply to the second variable:
. The linearity does not apply to the second variable:
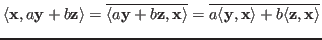
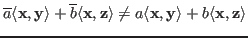
unless the coefficients are real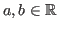 . As a special case,
when
. As a special case,
when 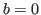 , we have
, we have
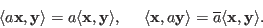
More generally we have
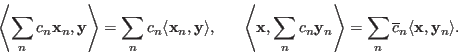
Some examples of the inner product are listed below:
- In an N-D vector space, the inner product, also called the
dot product, of two vectors
![${\bf x}=[x_1,\ldots,x_N]^T$](img54.png) and
and
![${\bf y}=[y_1,\ldots,y_N]^T$](img55.png) is defined as
is defined as
![\begin{displaymath}
\langle {\bf x}, {\bf y}\rangle={\bf x}^T\overline{{\bf y}}...
...ne{y}_N
\end{array} \right]=\sum_{n=1}^N x_n \overline{y}_n,
\end{displaymath}](img56.png)
where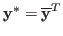 is the conjugate transpose of
is the conjugate transpose of 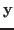 .
.
- In a space of 2-D matrices containing
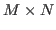 elements, the inner
product of two matrices
elements, the inner
product of two matrices 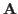 and
and 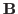 is defined as
is defined as
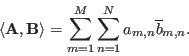
When the column (or row) vectors of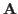 and
and 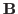 are concatenated
to form two
are concatenated
to form two 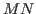 -D vectors, their inner product takes the same form as that
of two N-D vectors.
-D vectors, their inner product takes the same form as that
of two N-D vectors.
- In a function space, the inner product of two function vectors
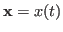 and
and 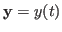 is defined as
is defined as
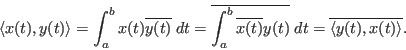
- The inner product of two random variables
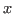 and
and 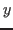 can be defined as
can be defined as
![\begin{displaymath}
\langle x,y\rangle=E[x\overline{y}].
\end{displaymath}](img67.png)
If the two random variables have zero means; i.e.,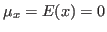 and
and
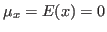 , the inner product above is also their covariance:
, the inner product above is also their covariance:
![\begin{displaymath}
\sigma^2_{xy}=E[(x-\mu_x)\overline{(y-\mu_y)}]=
E(x\overli...
...})-\mu_x\overline{\mu}_y=E(x\overline{y})=\langle x,y\rangle.
\end{displaymath}](img69.png)
The norm of a vector ![]() is defined below as a certain
measurement of its size or length:
is defined below as a certain
measurement of its size or length:
The norm
In particular, in an N-D unitary space, the norm of a vector
![]() is
is
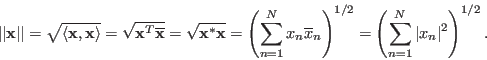
The total energy contained in this vector is its norm squared:
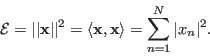
Similarly, in a function space, the norm of a function vector ![]() is defined as
is defined as
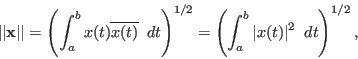
where the lower and upper integral limits
All such functions
The Cauchy-Schwarz inequality holds for any two vectors
![]() in an inner product space
in an inner product space ![]() :
:
Proof: If either ![]() or
or ![]() is zero,
is zero,
![]() , the theorem holds (an equality).
Otherwise, we consider the following inner product:
, the theorem holds (an equality).
Otherwise, we consider the following inner product:
where
Substituting these into the previous equation we get
The equation holds only if
The distance
![]() between two vectors
between two vectors ![]() and
and ![]() is a real constant that satisfies:
is a real constant that satisfies:
-
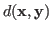 iff
iff
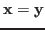
-
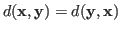
-
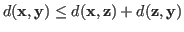
The angle between two vectors ![]() and
and ![]() is defined as
is defined as
Now the inner product of
In particular,
- if
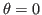 ,
, 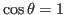 , then
, then 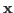 and
and 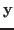 are collinear or linearly dependent, and the inner product is maximized:
are collinear or linearly dependent, and the inner product is maximized:
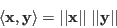
i.e., the Cauchy-Schwarz inequality becomes an equality. - if
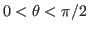 ,
,
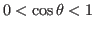 , we get the
Cauchy-Schwarz inequality:
, we get the
Cauchy-Schwarz inequality:
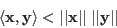
- if
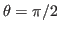 ,
, 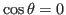 , then
, then 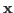 and
and 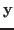 are orthogonal to each other, and the inner product is minimized:
are orthogonal to each other, and the inner product is minimized:
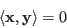
Two vectors ![]() and
and ![]() are orthogonal or
perpendicular to each other, denoted by
are orthogonal or
perpendicular to each other, denoted by
![]() ,
if their inner product is zero
,
if their inner product is zero
![]() , i.e.,
the angle between them is
, i.e.,
the angle between them is
The orthogonal projection of a vector ![]() onto another
vector
onto another
vector ![]() is defined as a vector
is defined as a vector
Note that
An inner product space is a vector space with inner product defined.
In particular, when the inner product is defined, ![]() is called
a unitary space and
is called
a unitary space and ![]() is called a Euclidean space.
is called a Euclidean space.
A metric space is a vector space ![]() in which the metric or
distance
in which the metric or
distance
![]() between any two vector (two points)
between any two vector (two points)
![]() and
and ![]() is defined.
is defined.
A sequence of points in a metric space
![]() is a
Cauchy sequence if it converges, i.e., for any
is a
Cauchy sequence if it converges, i.e., for any ![]() , there
exists an integer
, there
exists an integer ![]() so that the following is true for any
so that the following is true for any ![]() :
:
If the limit of any Cauchy sequence of points in the space is also in the space, the space is complete, referred to as a Cauchy space.