


Next: About this document ...
Up: Kernel PCA (KPCA)
Previous: Kernel PCA
Generally speaking, a kernel is a continuous function 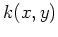 that takes
two arguments
that takes
two arguments 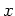 and
and 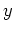 (real numbers, functions, vectors, etc.) and maps
them to a real value independent of the order of the arguments, i.e.,
(real numbers, functions, vectors, etc.) and maps
them to a real value independent of the order of the arguments, i.e.,
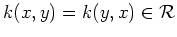 .
.
Examples:
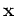 and
and 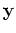 can be two n-dimensional vectors and
can be two n-dimensional vectors and
Or the kernel can be defined as
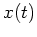 and
and 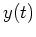 can be two functions and
can be two functions and
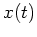 and
and 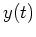 can be two functions and their convolution is
the kernel:
can be two functions and their convolution is
the kernel:
where 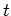 is a parameter.
is a parameter.
such that K(x, s) = K(s, x).
Ruye Wang
2007-03-26
![]() that takes
two arguments
that takes
two arguments ![]() and
and ![]() (real numbers, functions, vectors, etc.) and maps
them to a real value independent of the order of the arguments, i.e.,
(real numbers, functions, vectors, etc.) and maps
them to a real value independent of the order of the arguments, i.e.,
![]() .
.