The N-point DFT of time samples
![]() is defined as
(ignoring the coefficient
is defined as
(ignoring the coefficient ![]() for now):
for now):
![\begin{displaymath}X[n]=\sum_{m=0}^{N-1} x[m]e^{-j2\pi mn/N}=\sum_{m=0}^{N-1}x[m]w_N^{mn}
\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;(n=0, 1, \cdots, N-1) \end{displaymath}](img123.png)
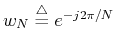 and it
is easy to show that
and it
is easy to show that ![\begin{displaymath}X[n]=\sum_{m=0}^{N-1} x[m]w_{N}^{mn}
=\sum_{m=0}^{M-1} x[2m]w_{2M}^{2mn}+\sum_{m=0}^{M-1} x[2m+1]w_{2M}^{(2m+1)n} \end{displaymath}](img130.png)
![\begin{displaymath}
X[n]= \sum_{m=0}^{M-1} x[2m]w_{M}^{mn}+
\sum_{m=0}^{M-1} x[...
...X_{even}[n]+X_{odd}[n] w_{2M}^n,\;\;\;\;\;\;\;(n=0,\cdots,M-1)
\end{displaymath}](img132.png) |
(1) |
![\begin{displaymath}X_{even}[n]\stackrel{\triangle}{=}\sum_{m=0}^{N-1} x[2m]w_{M}...
...d}[n]\stackrel{\triangle}{=}\sum_{m=0}^{N-1} x[2m+1]w_{M}^{mn} \end{displaymath}](img133.png)
Here we let the index ![]() cover only the first half of the original range of
the DFT,
cover only the first half of the original range of
the DFT,
![]() . The second half can be obtained by
replacing
. The second half can be obtained by
replacing ![]() in Eq. (1) by
in Eq. (1) by ![]() :
:
![\begin{displaymath}X_{even}[n+M]=\sum_{m=0}^{M-1} x[2m]w_{M}^{m(n+M)}
=\sum_{m=0}^{M-1} x[2m]w_{M}^{mn}=X_{even}[n]
\end{displaymath}](img139.png)
| (2) |
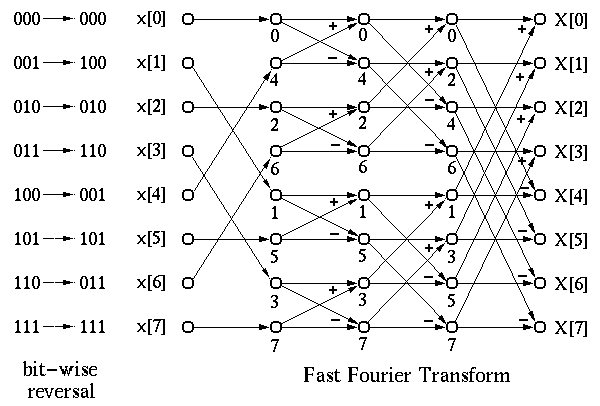
The N-point DFT can now be obtained from Eqs. (1), (2), once ![]() and
and ![]() are available. However, since
are available. However, since ![]() and
and ![]() are N/2-point DFTs, they can be obtained the same way. This process goes
on recursively until finally only 1-point DFTs are needed, which are just
the time samples themselves. Therefore, the operations of an N-point DFT can
be symbolically represented by the following diagram. The complexity is
therefore reduced from
are N/2-point DFTs, they can be obtained the same way. This process goes
on recursively until finally only 1-point DFTs are needed, which are just
the time samples themselves. Therefore, the operations of an N-point DFT can
be symbolically represented by the following diagram. The complexity is
therefore reduced from ![]() to
to
![]() .
.