


Next: About this document ...
E84 Home Work 6
- The resistance
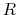 of a circuit is a real value which can be measured
by a multimeter. However, the impedance
of a circuit is a real value which can be measured
by a multimeter. However, the impedance 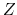 of a component in the circuit is
complex which cannot be measured directly. Instead, one can use an oscilloscope
to find sinusoidal voltage
of a component in the circuit is
complex which cannot be measured directly. Instead, one can use an oscilloscope
to find sinusoidal voltage 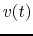 across and current
across and current 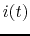 through the component,
and then obtain the impedance as the ratio between the complex representations of
the voltage and current. Suppose we find:
through the component,
and then obtain the impedance as the ratio between the complex representations of
the voltage and current. Suppose we find:
Find the impedance (both resistance and reactance) and the admittance (both
conductance and susceptance) of the circuit.
- A voltage
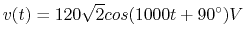 (volt) is applied to
a resistor
(volt) is applied to
a resistor 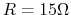 , a capacitor
, a capacitor 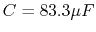 and an inductor
and an inductor 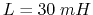 connected in parallel. Find the over all steady state current
connected in parallel. Find the over all steady state current 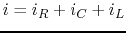 by phasor method.
by phasor method.
- A voltage
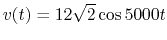 (volt V) is applied to a circuit
composed of two branches in parallel. One branch has a capacitor
(volt V) is applied to a circuit
composed of two branches in parallel. One branch has a capacitor 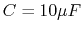 ,
while the other has a resistor
,
while the other has a resistor 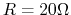 and an inductor
and an inductor 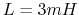 in series.
Using phasor method, find the impedances
in series.
Using phasor method, find the impedances 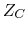 and
and 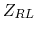 of the two branches,
and then the overall combined impedance
of the two branches,
and then the overall combined impedance 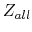 of the circuit. Then find
the steady state current
of the circuit. Then find
the steady state current 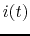 through the circuit.
through the circuit.
- Solve the problem above again but this time use the admittances
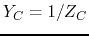 ,
,
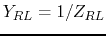 ,
,
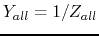 (instead of the
impedances
(instead of the
impedances 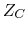 ,
, 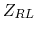 ,
, 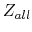 ). Recall that Ohm's law becomes
). Recall that Ohm's law becomes
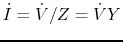 . (Make sure all impedances you found in
previous problem are correct before you find the admittances as their
reciprocals.)
. (Make sure all impedances you found in
previous problem are correct before you find the admittances as their
reciprocals.)
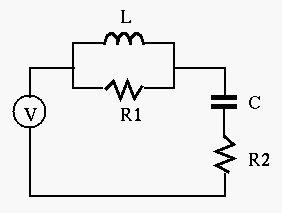
- Find the output voltage
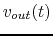 across the right most branch
containing
across the right most branch
containing 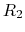 and
and 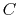 , when
, when 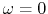 and
and
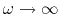 and the input
and the input
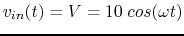 , assuming
, assuming 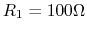 ,
,
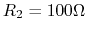 ,
, 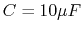 and
and 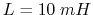 .
.



Next: About this document ...
Ruye Wang
2008-03-05

