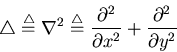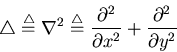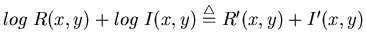Next: Homomorphic Filtering Algorithm
Up: Computational Models of Color
Previous: Land's Retinex Theory
A different computational model was proposed by Horn to account for the color
constancy. This model is based on the same assumption that in general the
illumination is a low spatial frequency signal while the reflectance is a high
spatial frequency signal. To separate the high frequency components from the
signal, a differential operation, can be considered. Since we want to
treat edges of different orientations equally, the first order partial
derivatives with respect to the two spatial directions x and y are not
the best candidate as they are not rotationally symmetric. Therefore the second
order spatial derivative, the Laplacian operator, is used:
- Take logarithm of the input light signal so that reflectance and
illumination become additive:
- Apply Laplacian operator to
L'(x,y)=R'(x,y)+I'(x,y)
- Threshold
As we assume the illumination as a spatial function is much more homogeneous
than the reflectance, the Laplas of the illumination
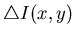 is
small and therefore does not pass the threshold T.
is
small and therefore does not pass the threshold T.
- Take inverse Laplacian operation
where R'(x,y) is the desired reflectance that can be obtained by solving
this Poisson's equation using convolution
where
- Take exponential operation
R(x,y)=exp[ R'(x,y) ]



Next: Homomorphic Filtering Algorithm
Up: Computational Models of Color
Previous: Land's Retinex Theory
Ruye Wang
2000-04-25