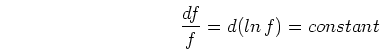Next: Spatial sampling
Up: Image Digitization
Previous: Image Digitization
The continuous range of light intensity 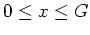 received by the
digital image acquisition system need be quantized to
received by the
digital image acquisition system need be quantized to 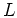 gray levels
(e.g.,
gray levels
(e.g., 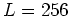 ).
).
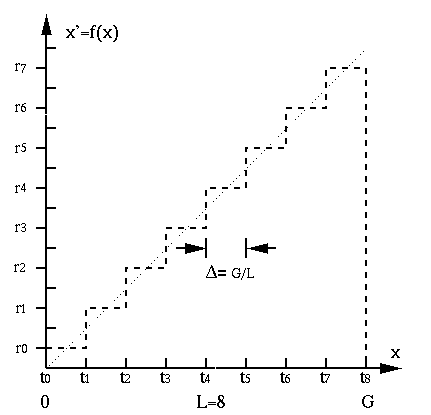
- Uniform distribution
Define
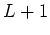 boundaries
boundaries
where
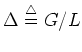 . And define the
. And define the 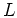 discrete gray
levels to represent the L intervals:
discrete gray
levels to represent the L intervals:
Then the quantization can be defined as a function
- Mean square error optimization
Define mean square error of the quantization process as
where 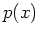 is distribution of input intensify
is distribution of input intensify 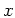 . The optimal quantization
in terms of
. The optimal quantization
in terms of 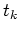 and
and 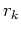 can be found by minimizing
can be found by minimizing 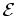 , by solving
, by solving
This method requires 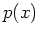 to be known. The previous quantization is optimal when
to be known. The previous quantization is optimal when
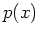 is a uniform distribution.
is a uniform distribution.
- Contrast equalization
The perceived contrast is a function of the intensity. Specifically, we
perceive the same contrast between the object and its surrounding if
i.e., we are less sensitive to contrast when the intensity is high. (As an example,
consider the perceived brightness of a 3-way bulb with 50, 100 and 150 Watts.)
Consequently, the contrast can be defined as a logarithmic function of the
intensity:
As shown in the figure, to perceive the same contrast, larger intensity
difference is needed for higher intensity regions than lower ones.

To most efficiently use the limited number of gray levels available, we can
allocate more gray levels in the low intensity region where our eye is more
sensitive to contrast) than in high intensity region.



Next: Spatial sampling
Up: Image Digitization
Previous: Image Digitization
Ruye Wang
2009-09-03
![]() received by the
digital image acquisition system need be quantized to
received by the
digital image acquisition system need be quantized to ![]() gray levels
(e.g.,
gray levels
(e.g., ![]() ).
).
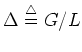 . And define the
. And define the 
![\begin{displaymath}{\cal E} = E[ (x-x')^2]=\int_{-\infty}^\infty (x-x')^2 p(x)dx=
\sum_{i=0}^{L-1} \int_{t_i}^{t_{i+1}} (x-r_i)^2 p(x)dx \end{displaymath}](img11.png)